Unveiling The Fascinating World Of Protozoa: Comprehensive Guide To Their Characteristics
Protozoa, the microscopic single-celled organisms, form an integral part of the ecosystem and play a significant role in maintaining ecological balance. These organisms are fascinating due to their diverse characteristics of protozoa, which include their ability to move, feed, and reproduce independently. Protozoa are found in various habitats, from freshwater ponds to the human gut, showcasing their adaptability and resilience. Understanding the characteristics of protozoa is crucial for comprehending their ecological importance and potential implications in health and disease.
As we delve deeper into the world of protozoa, we uncover their unique features that set them apart from other microorganisms. Protozoa exhibit a wide range of shapes and sizes, with some species being free-living while others are parasitic. Their modes of locomotion, such as cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia, enable them to navigate through different environments. Moreover, their feeding mechanisms, reproductive strategies, and survival tactics contribute to their success as one of the most ancient groups of organisms on Earth.
Protozoa are not only scientifically intriguing but also have practical implications for human health and the environment. Some species of protozoa are responsible for serious diseases, such as malaria and amoebic dysentery, while others serve as bioindicators of water quality. By exploring the characteristics of protozoa, we gain insights into their ecological roles and potential applications in biotechnology and medicine. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of protozoa, focusing on their defining characteristics, ecological significance, and impact on human health.
Read also:Lauren Boebert Tim Walz And The Detroit Quote A Comprehensive Analysis
What Are Protozoa?
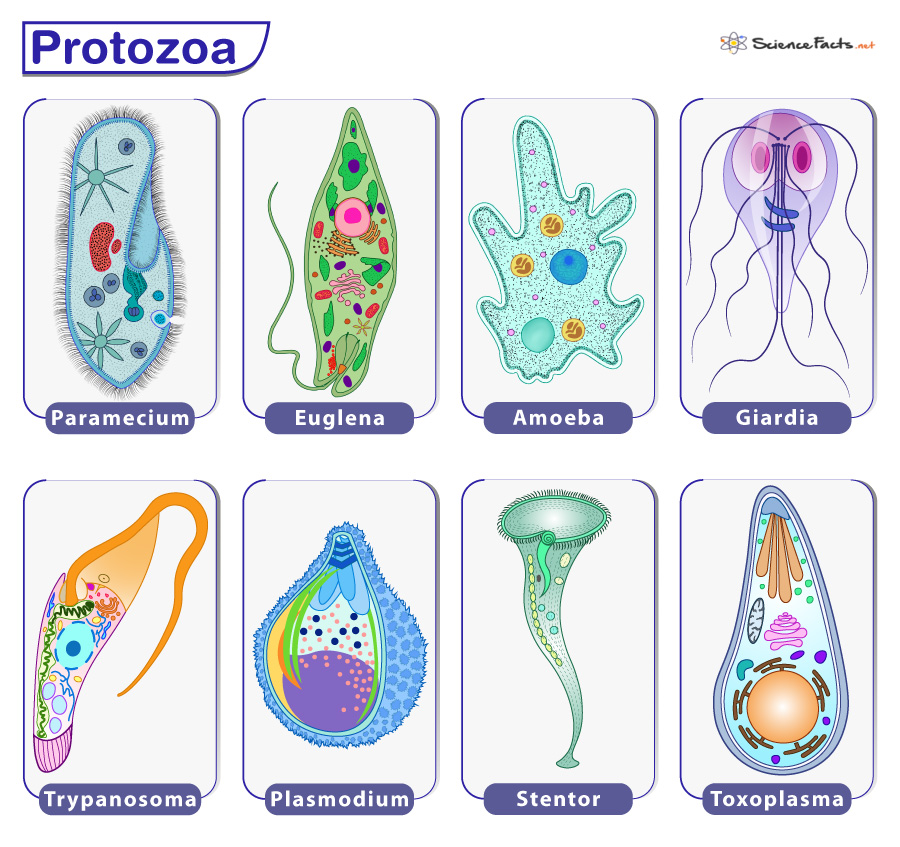
Protozoa are single-celled organisms that belong to the kingdom Protista. They are eukaryotic, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Protozoa can be found in almost every aquatic environment, as well as in moist soils and as parasites in animals and humans. They are classified into four main groups based on their mode of locomotion: amoeboids, ciliates, flagellates, and sporozoans. Each group exhibits distinct characteristics of protozoa that define their ecological roles and interactions with other organisms.
How Do Protozoa Move?
Motion is one of the defining characteristics of protozoa, enabling them to search for food, avoid predators, and reproduce. Amoeboids move by extending pseudopodia, which are temporary projections of their cytoplasm. Ciliates use hair-like structures called cilia to propel themselves through water, while flagellates rely on whip-like flagella for locomotion. Sporozoans, on the other hand, are non-motile during their infective stages but may exhibit movement during their life cycle. The diversity in locomotion reflects the adaptability of protozoa to various environments.
Why Are Protozoa Important in Ecosystems?
Protozoa play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems. As primary consumers, they feed on bacteria, algae, and other small organisms, helping to control their populations. In turn, protozoa serve as a food source for larger organisms, contributing to the energy flow within the ecosystem. Additionally, protozoa contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and releasing essential nutrients back into the environment. Their importance in ecosystems underscores the need to study the characteristics of protozoa to understand their broader ecological implications.
What Are the Main Characteristics of Protozoa?
- Single-celled structure
- Eukaryotic organisms
- Diverse modes of locomotion
- Variety in feeding mechanisms
- Complex reproductive strategies
Which Characteristics of Protozoa Define Their Feeding Habits?
The feeding habits of protozoa are closely tied to their structural and functional characteristics. Some protozoa are holozoic, meaning they ingest solid food particles, while others are saprotrophic, absorbing nutrients from their surroundings. Protozoa employ different mechanisms for capturing prey, such as engulfing bacteria through phagocytosis or trapping food particles with cilia. These feeding habits allow protozoa to thrive in diverse environments and contribute to the cycling of nutrients in ecosystems.
Ecological Significance of Protozoa
Protozoa are vital components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, influencing nutrient cycling, energy flow, and population dynamics. In aquatic ecosystems, protozoa act as grazers, controlling the populations of bacteria and algae. This grazing activity helps maintain water clarity and prevents algal blooms, which can have detrimental effects on aquatic life. Protozoa also serve as prey for larger organisms, forming an integral part of the food web. Understanding the ecological significance of protozoa requires a thorough examination of their characteristics of protozoa and interactions with the environment.
What Role Do Protozoa Play in Disease Transmission?
While many protozoa are harmless, some species are pathogenic and responsible for serious diseases in humans and animals. Malaria, caused by the protozoan Plasmodium, is one of the most well-known examples of protozoan-borne diseases. Other diseases include amoebic dysentery, caused by Entamoeba histolytica, and giardiasis, caused by Giardia lamblia. The transmission of these diseases often involves vectors, such as mosquitoes, or contaminated water sources. By studying the characteristics of protozoa, scientists can develop strategies to prevent and control protozoan infections.
Read also:Beyonceacute Weight 2025 A Comprehensive Guide To Her Fitness Journey And Lifestyle
Characteristics of Protozoa: Reproduction and Survival
Protozoa exhibit a variety of reproductive strategies, including binary fission, budding, and sexual reproduction. Binary fission is the most common method, where a protozoan divides into two identical daughter cells. Some species, like Plasmodium, undergo complex life cycles involving both asexual and sexual reproduction. These reproductive strategies enhance the survival of protozoa in changing environments. Additionally, protozoa have developed mechanisms to survive adverse conditions, such as forming cysts, which allow them to withstand desiccation and extreme temperatures.
How Do Characteristics of Protozoa Impact Their Classification?
The classification of protozoa is based on their structural and functional characteristics. The four main groups—amoeboids, ciliates, flagellates, and sporozoans—are defined by their mode of locomotion, feeding habits, and reproductive strategies. Advances in molecular biology have provided new insights into the evolutionary relationships among protozoa, leading to refinements in their classification. Understanding the characteristics of protozoa is essential for accurate classification and identification of these organisms.
Conclusion: The Importance of Studying Protozoa
Protozoa are fascinating microorganisms with diverse characteristics that make them vital to ecosystems and human health. Their ability to move, feed, and reproduce independently sets them apart from other microorganisms. By studying the characteristics of protozoa, scientists gain valuable insights into their ecological roles, disease-causing potential, and evolutionary history. As we continue to explore the world of protozoa, we uncover new possibilities for harnessing their potential in biotechnology and medicine. This comprehensive guide highlights the importance of protozoa and encourages further research into their unique characteristics.
Table of Contents
- What Are Protozoa?
- How Do Protozoa Move?
- Why Are Protozoa Important in Ecosystems?
- What Are the Main Characteristics of Protozoa?
- Which Characteristics of Protozoa Define Their Feeding Habits?
- Ecological Significance of Protozoa
- What Role Do Protozoa Play in Disease Transmission?
- Characteristics of Protozoa: Reproduction and Survival
- How Do Characteristics of Protozoa Impact Their Classification?
- Conclusion: The Importance of Studying Protozoa